MSU Researchers Invent Foot Position Detection System Using LDR Sensors
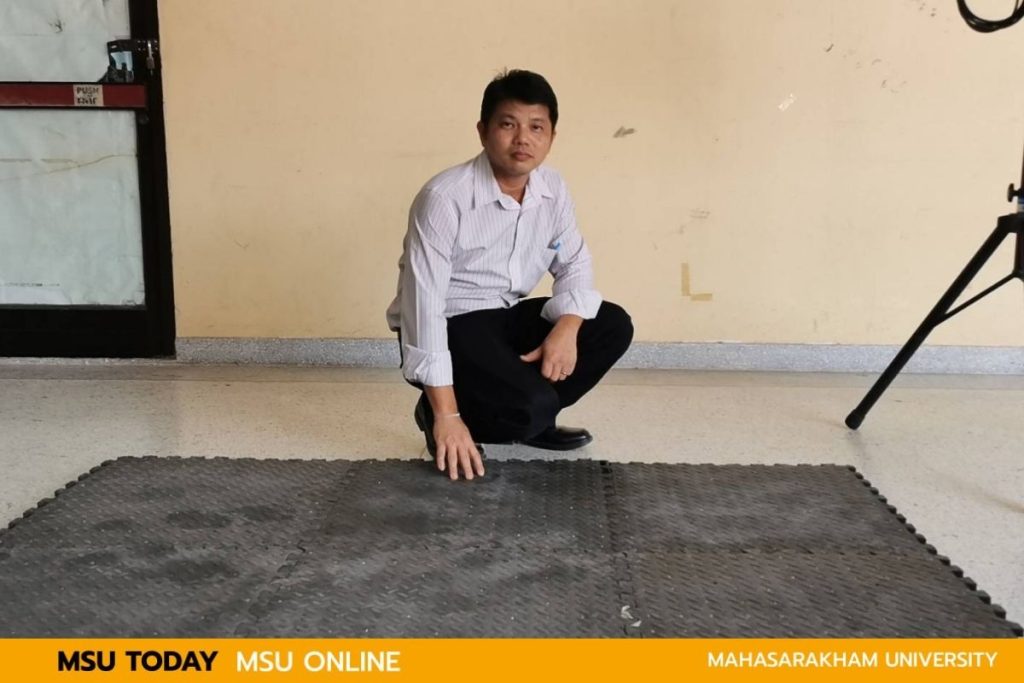
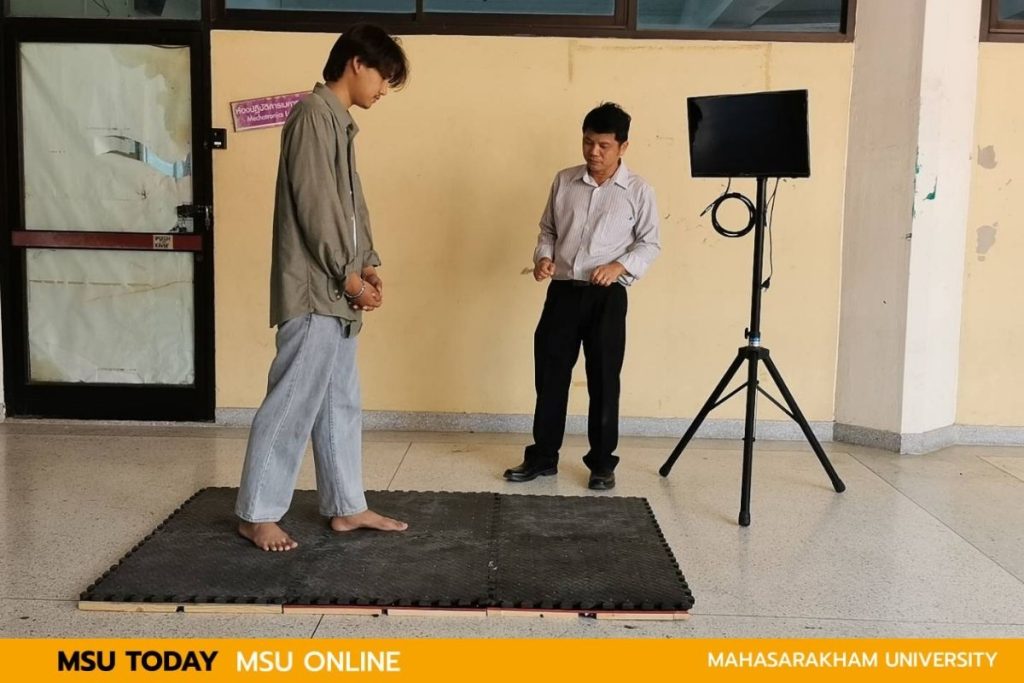
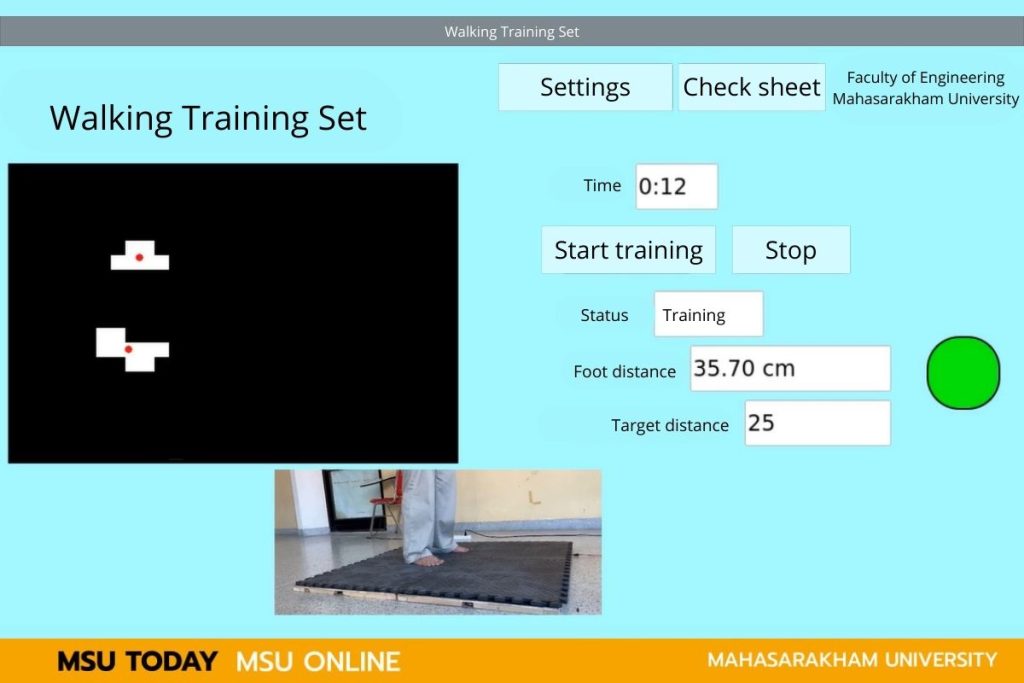
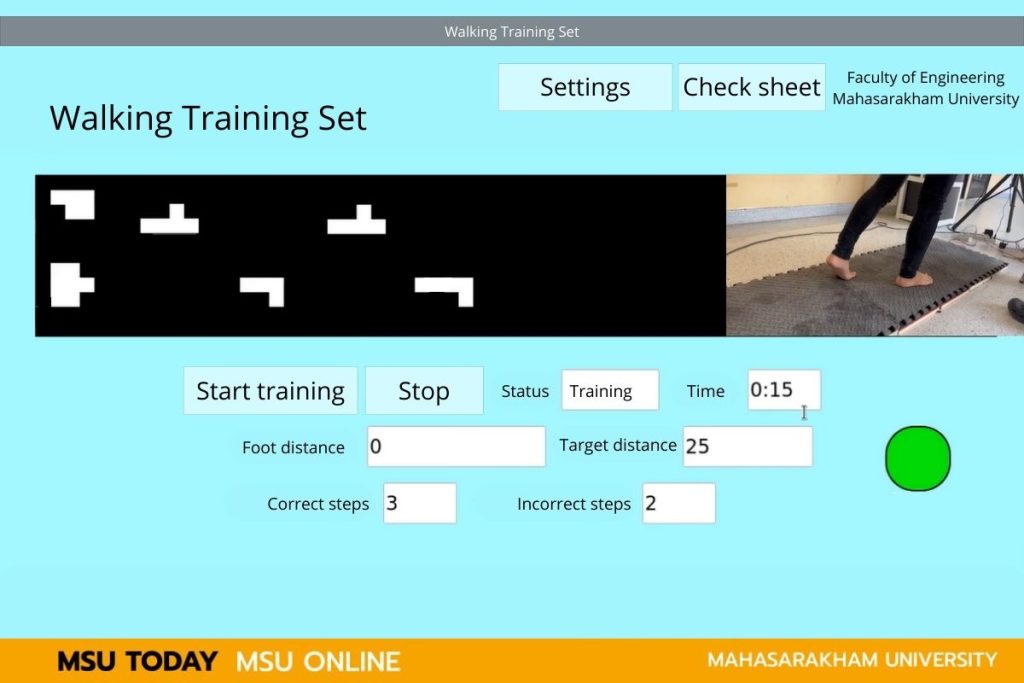
Researchers at MSU invented a foot position detection system on areas equipped with LDR sensors as part of a walking training process for rehabilitation and enhancing the ability to control the body for patients with diseases affecting the brain, spinal cord, nerves, or leg injuries, enabling them to walk safely again. The system is developed under the supervision of Assoc.Prof. Kiattisin Kanjanawanishkul, a lecturer in the Department of Mechatronics Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, MSU.
Title of the Work
Foot Position Detection System on Areas Equipped with LDR Sensors
Research Background
Walking training is part of the physical rehabilitation process to improve bodily control for patients with diseases affecting the brain, spinal cord, nerves, or leg injuries, enabling them to walk again. This process involves learning how to walk under the supervision of a physiotherapist or rehabilitation specialist. During the training, physical therapists aim to assess foot contact, weight distribution symmetry between both sides, step length, and walking speed. Currently, physiotherapists assess patients through observation and experience, which can lead to errors and impact the planning of the training. Therefore, developing a foot position detection system helps physiotherapists evaluate walking training accurately and in real time.
Another application of the foot position detection system is the assessment of the capabilities of children, the elderly, or athletes. For example, footstep training in primary school children is crucial for physical and mental development, as it improves balance and responsiveness. In athletes, the system can be used to train movement and rapid direction changes, enhancing neuromuscular coordination. In the case of the elderly, there is a stepping exercise program consisting of walking slowly in the forward, sideways, back and diagonal directions.